Playbook configuration¶
Warning
This page contains out-of-date information. It is currently being updated to reflect Robusta’s new configuration format.
Enabling playbooks¶
To activate a playbook, the playbook name must be listed in values.yaml and the playbook directory must then be loaded.
Here is an excerpt from values.yaml which enables three playbooks:
playbooks:
- name: "python_profiler"
- name: "restart_loop_reporter"
- name: "deployment_babysitter"
Playbooks sinks¶
With Robusta, playbooks results can be sent to one or more sinks.
The deployment_babysitter playbook’s data will appear as follows on the different sinks:
robusta ui:
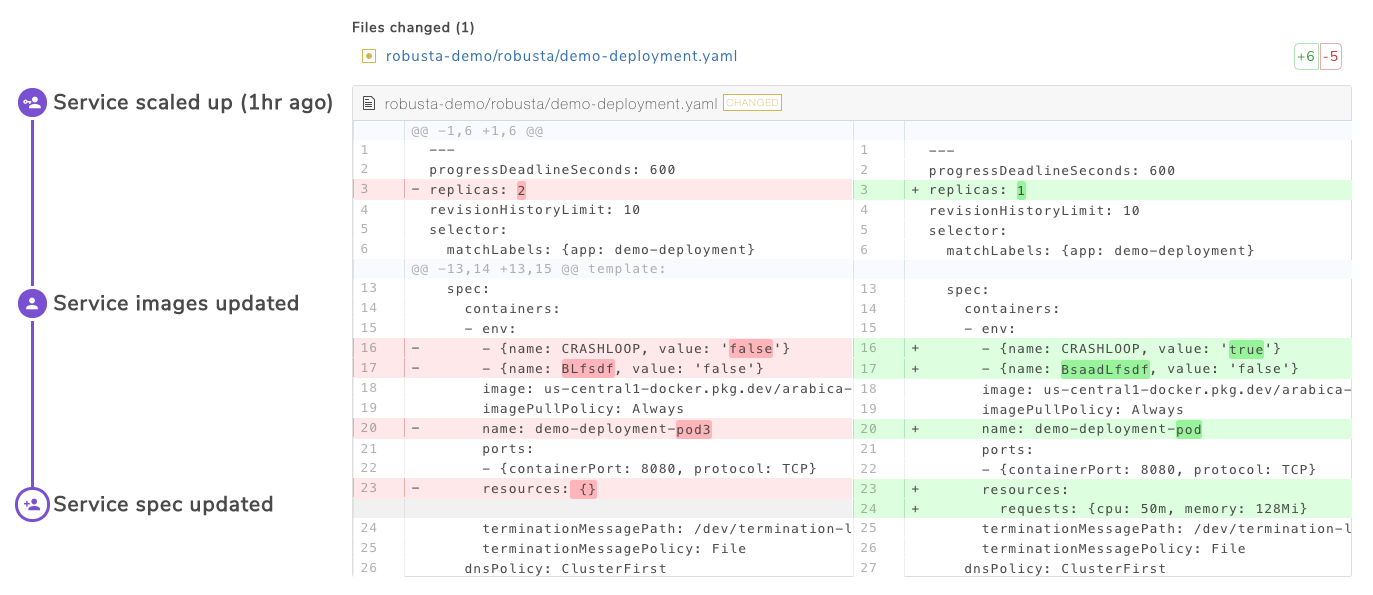
slack:
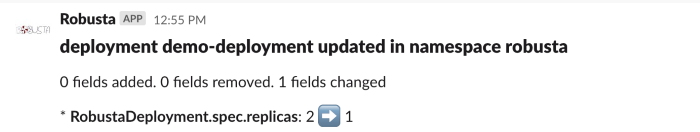
kafka:

datadog:

Currently four sink types are supported:
slack: - Send playbooks results to Slack channel
robusta: - Send playbooks results Robusta’s dedicated UI
kafka: - Send playbooks results to a kafka topic
datadog: - Send playbooks results to a DataDog events api
The Helm chart only exposes the ability to configure one Robusta sink and one Slack sink. See the Helm chart’s values.yaml file for reference.
Playbook parameters¶
Many playbooks expose variables which can be set in values.yaml. Here is an example of how you can configure the restart_loop_reporter playbook.
This is a playbook which adds annotations to grafana every time that a deployment’s version changes. (The version is calculated according to docker image tags.)
playbooks:
- name: "add_deployment_lines_to_grafana"
action_params:
grafana_dashboard_uid: "uid_from_url"
grafana_api_key: "grafana_api_key_with_editor_role"
grafana_service_name: "grafana.namespace.svc.cluster.local:3000"
The above enables the playbook and customizes it with three variables that the playbook requires. You can find a list of playbook variables in the documentation of each playbook.
Trigger Params¶
Playbooks can be customized so that they only run when certain conditions apply. Here we further customize the playbook from the previous example so that it only runs for deployments whose name starts with “MyApp”:
playbooks:
- name: "add_deployment_lines_to_grafana"
action_params:
grafana_dashboard_uid: "uid_from_url"
grafana_api_key: "grafana_api_key_with_editor_role"
grafana_service_name: "grafana.namespace.svc.cluster.local:3000"
trigger_params:
name_prefix: "MyApp"
Currently all playbooks for Kubernetes changes accept the trigger_params name_prefix and namespace_prefix.
All playbooks for Prometheus alerts accept the trigger_params pod_name_prefix and instance_name_prefix.
If you need support for additional trigger_params, please contact us and we will be happy to add additional trigger_params for your use case.
Enabling a playbook multiple times¶
You can enable a playbook multiple times with different configurations. For example:
playbooks:
- name: "add_deployment_lines_to_grafana"
action_params:
grafana_dashboard_uid: "dashboard1"
grafana_api_key: "grafana_api_key_with_editor_role"
grafana_service_name: "grafana.namespace.svc.cluster.local:3000"
trigger_params:
name_prefix: "App1"
- name: "add_deployment_lines_to_grafana"
action_params:
grafana_dashboard_uid: "dashboard2"
grafana_api_key: "grafana_api_key_with_editor_role"
grafana_service_name: "grafana.namespace.svc.cluster.local:3000"
trigger_params:
name_prefix: "App2"
Global playbook parameters¶
Warning
This section describes the internal Robusta active_playbooks.yaml file. This functionality is not yet exposed in the Helm chart’s values.yaml
In the previous example the playbook variables grafana_api_key and grafana_service_name were defined multiple times with the same value.
To avoid repeating yourself you can define trigger_params and parameters globally for all playbooks. They will be applied to any playbook where they are valid:
global_config:
cluster_name: "my-staging-cluster"
grafana_api_key: "grafana_api_key_with_editor_role"
grafana_service_name: "grafana.namespace.svc.cluster.local:3000"
active_playbooks:
- name: "add_deployment_lines_to_grafana"
action_params:
grafana_dashboard_uid: "dashboard1"
trigger_params:
name_prefix: "App1"
- name: "add_deployment_lines_to_grafana"
action_params:
grafana_dashboard_uid: "dashboard2"
trigger_params:
name_prefix: "App2"
Note
The cluster_name is a required parameter, since it’s used for sinks as the cluster identifier. cluster_name should be unique among different clusters
Advanced playbook sinks configuration¶
Warning
This section describes the internal Robusta active_playbooks.yaml file. This functionality is not yet exposed in the Helm chart’s values.yaml
To use sinks, first define the available named sinks in active_playbooks.yaml.
sinks_config:
- sink_name: "robusta ui"
sink_type: "robusta"
params:
token: "MY ROBUSTA ACCOUNT TOKEN"
- sink_name: "alerts slack"
sink_type: "slack"
params:
api_key: "ROBUSTA SLACK API KEY"
slack_channel: "robusta alerts channel"
- sink_name: "my kafka sink"
sink_type: "kafka"
params:
kafka_url: "localhost:9092"
topic: "robusta-playbooks"
- sink_name: "datadog events"
sink_type: "datadog"
params:
api_key: "MY DATADOG ACCOUNT API KEY"
Note
In order to get a Slack key run: robusta integrations slack.
By default, all playbooks will forward the results to the default sinks.
The default sinks are defined in the global_config section of active_playbooks.yaml.
global_config:
sinks:
- "robusta ui"
- "alerts slack"
The default sinks list can be overridden, per playbook:
- name: "add_deployment_lines_to_grafana"
sinks:
- "my kafka sink"
action_params:
grafana_dashboard_uid: "uid_from_url"
grafana_api_key: "grafana_api_key_with_editor_role"
grafana_service_name: "grafana.namespace.svc.cluster.local:3000"