Event Hierarchy¶
When configuring Robusta as a user, you define triggers in values.yaml but when writing playbook
actions you deal with events.
This page explains the connection between the two.
Lifecycle of a Robusta event¶
A pod changes
The API Server notifies Robusta
Robusta checks if any triggers like
on_pod_updateare activated by the pod changeIf yes, Robusta calls that trigger
The trigger converts data from the APIServer to a concrete event like
PodChangeEventThe
PodChangeEventis passed to all playbook actions
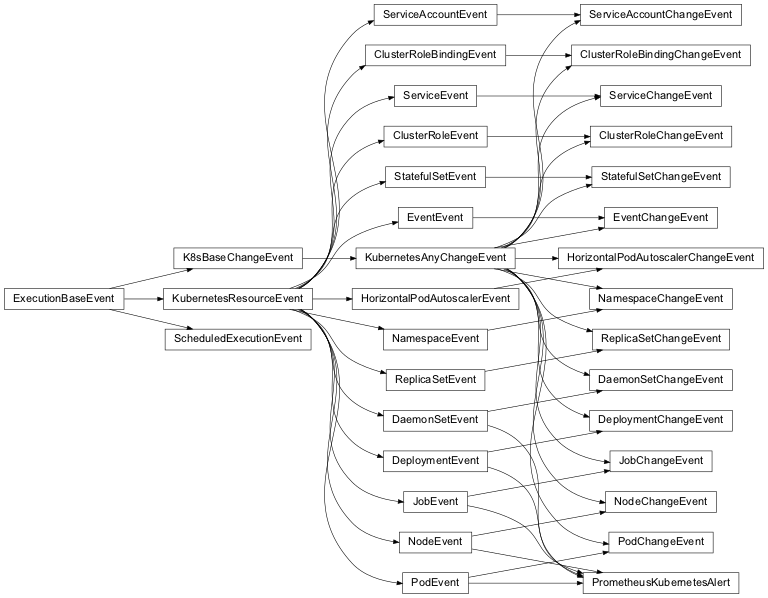
Here is the Robusta event hierarchy:
Support manual triggers¶
You’re writing a playbook action and you’d like to support Manual Triggers. It’s easy.
All classes above with names like PodEvent support manual triggers automatically. When running the manual trigger
specify the pod’s name and Robusta will generate an artificial event.
On the other hand, events like PodChangeEvent don’t support manual triggers. PodChangeEvent cannot be generated
artificially because it requires two versions of the pod - a before and after version.